Pyrheliometers
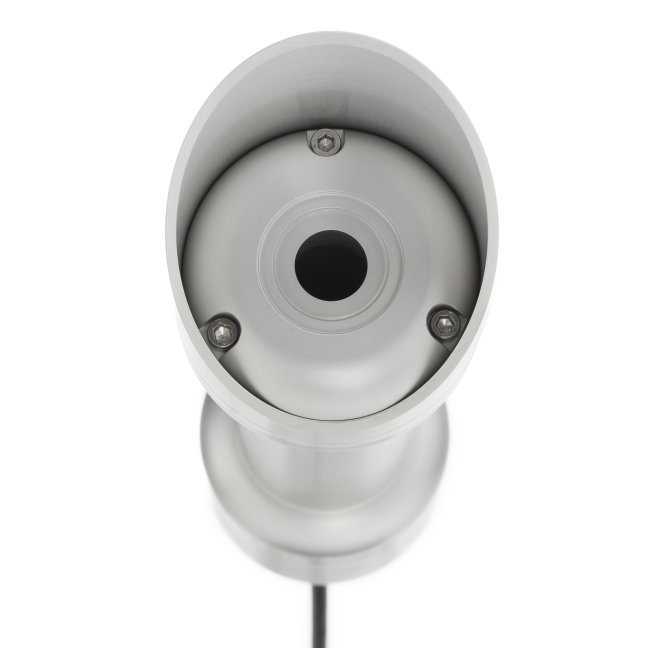
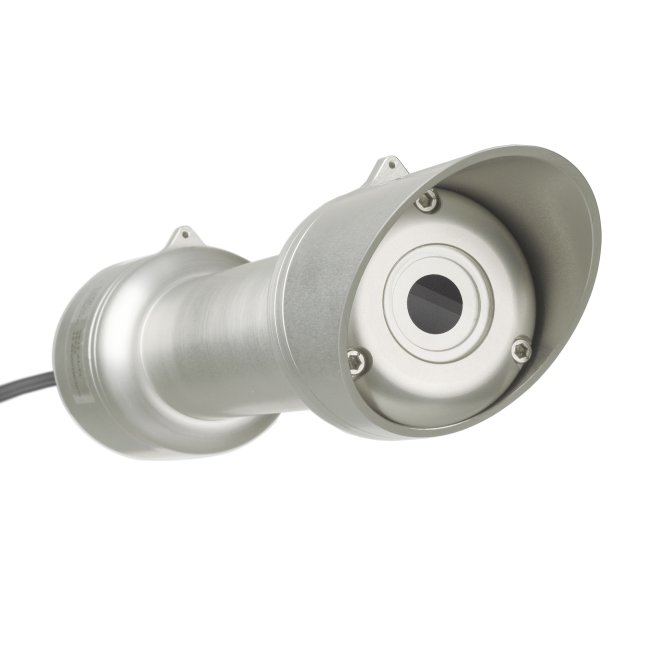
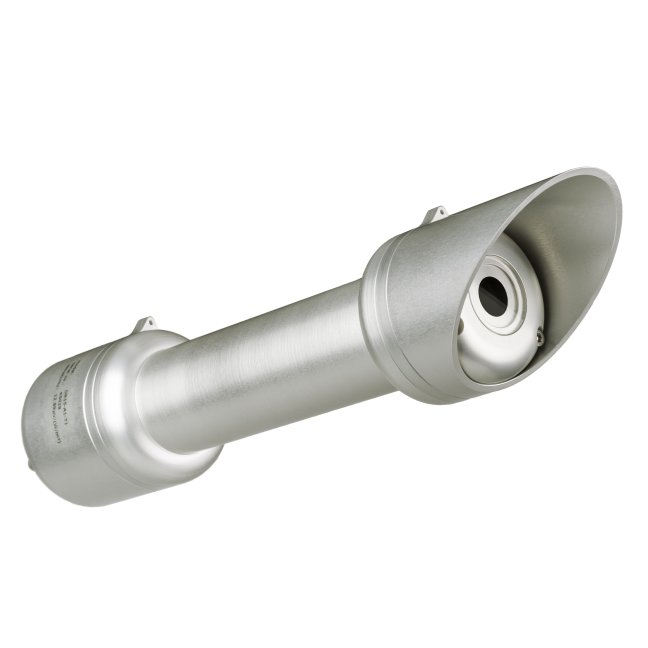
Pyrheliometers are direct (normal incidence) solar radiation sensors, used in outdoor PV / CPV and CSP system performance monitoring, solar energy surveys and scientific meteorological and climate observations. A pyrheliometer is usually used in tracker-mounted operation, to keep the instrument aimed at the sun.
Hukseflux offers a complete range of pyrheliometers. High data availability is attained by heating of the front window. This suppresses dew and frost deposition. Top model DR30-D1 pyrheliometer has superior window heating and an internal tilt sensor to check tracker performance.
Applications of pyrheliometers
A pyrheliometer is used to measure Direct Normal Irradiance (DNI). DNI is defined as the solar radiant flux collected by a plane unit surface normal to the axis pointing towards the centre of the sun, within an optical angular aperture. DNI is composed of the solar irradiance within the extent of the solar disk (half-angle 0.266 ° ± 1.7 %) plus some circumsolar radiation.
Frequently asked questions
What is the difference between a pyrheliometer and a pyranometer?
A pyranometer measures hemispherical solar radiation. When measuring in the horizontal plane this is called Global Horizontal Irradiance (GHI). When measuring in “plane of array”, next to PV panels, this is called plane of array POA irradiance.
A pyrheliometer is used to measure Direct Normal Irradiance (DNI). DNI is defined as the solar radiant flux collected by a plane unit surface normal to the axis pointing towards the centre of the sun, within an optical angular aperture. DNI is composed of the solar irradiance within the extent of the solar disk (half-angle 0.266 ° ± 1.7 %) plus some circumsolar radiation.